Senior Strength Training unveils its age-defying secret as we navigate the intricacies of aging today, an often overlooked yet powerful tool emerging. This article aims to unearth the transformative benefits of this practice and its potential for reshaping the aging narrative.
Understanding Senior Strength Training:
Senior Fitness Training Dynamics
Aging is a natural process that introduces several physiological changes. These alterations often decrease muscle mass, Strength, and overall mobility. Senior strength training involves tailored exercises to counteract these changes and promote physical wellness.
The Science of Sarcopenia
Sarcopenia, the age-related loss of muscle mass and Strength, is a chief concern among seniors. It contributes to reduced mobility, increased vulnerability to injury, and decreased overall health. However, regular strength training proves to be an effective antidote to this process.
Types of Strength Training:
As individuals age, their needs and preferences for exercise may change, and not all workouts may be suitable for seniors. However, it’s okay since diverse approaches to strength training are ideal for seniors. Various methodologies exist to cater to different preferences and physical capabilities, from utilizing resistance bands to engaging in bodyweight exercises or even incorporating weight training.
Agile Strength Training
Agile Strength entails swiftly changing directions with precision and power and managing controlled acceleration and deceleration in response to external stimuli or individuals in your vicinity.
Endurance Strength Training
Endurance strength, or muscular endurance, refers to your capacity to handle lighter loads over extended durations. Improving your endurance strength prolongs the duration before experiencing fatigue during exercise, enabling you to sustain performance without compromising form. The optimal approach to enhance endurance in strength training involves prioritizing high-repetition, low-weight workouts utilizing only bodyweight or light resistance.
Explosive Strength Training
Explosive Strength pertains to the muscles’ capability to exert maximum force within a minimal timeframe. When discussing explosive strength strength, the focus lies on the interplay between force and velocity.
Maximum Strength Training
Maximum Strength indicates the highest weight you can lift for a single repetition in exercises such as bench press (for assessing upper body strength) or deadlift (for evaluating lower body maximum strength).
Speed Strength Training
Speed Strength measures your quickness. This form of StrengthStrength proves beneficial in team sports or competitive events, granting you an advantage in contests. Speed strength can also enhance your reaction time, enabling you to respond swiftly to situations such as catching a thrown ball.
Starting Strength Training
Starting Strength pertains to the amount of force you can generate right at the onset of movement, such as during a track start or when a football lineman is in position before the ball is snapped, explains Schaper. It measures the power or force you can muster without the aid of momentum, akin to getting up from a chair after prolonged sitting. Individuals with weaker starting strength may need help in such movements.
Relative Strength Training
Relative Strength refers to your strength-to-weight ratio, indicating how strong you are close to your size. It quantifies your gains, so an increase signifies an improvement in your performance.

The Best Strength Training or Exercises for Seniors:
Physical activity is vital for older adults, yet it can be challenging to determine where to start. Returning to an active lifestyle after a period of inactivity can feel overwhelming. Additionally, once suitable exercises may no longer be appropriate for older individuals.
Before embarking on an exercise routine, it is essential to consult with a physician to confirm your suitability for physical activity and to identify exercises suitable for your current fitness level.
Water Aerobics
Water aerobics has recently gained significant popularity, especially among seniors. Exercising in water is particularly beneficial for individuals dealing with arthritis and joint pain, as the buoyancy of water reduces stress on the joints. Additionally, water provides natural resistance, eliminating the need for weights in strength training. Water aerobics exercises effectively improve Strength, flexibility, and balance with minimal impact on the body. Recommended water aerobics exercises for seniors include aqua jogging, flutter kicking, leg lifting, standing water push-ups, and arm curls.
Chair Yoga
Chair yoga is a gentle exercise that enhances muscle strength, mobility, balance, and flexibility, all vital aspects of senior health. It offers accessibility and reduces stress on muscles, joints, and bones compared to traditional yoga practices. Moreover, chair yoga contributes to improved mental well-being in older adults. Regular participants experience enhanced sleep quality, reduced depression rates, and overall well-being. Recommended chair yoga exercises for seniors include overhead stretch, seated cow stretch, seated cat stretch, seated mountain pose, and seated twist.
Resistance Bands and Elastic Rubber
Resistance bands and elastic rubber strips provide added resistance to workouts while minimizing stress on the body. They offer user-friendly and accessible exercise options, particularly suitable for beginners. Their growing popularity among seniors is due to the relatively low initial materials costs, making resistance band workouts ideal for home exercise. Additionally, these exercises effectively strengthen the core, leading to improved posture, mobility, and balance. Recommended resistance band workouts for seniors include leg press, triceps press, lateral raise, bicep curl, and band pull apart.
Pilates
Pilates, a well-known low-impact exercise method, originated a century ago. Pilates workouts emphasize breathing, alignment, concentration, and core strength, often incorporating mats, Pilates balls, and other inflatable accessories to build Strength without the strain of high-impact exercises. Pilates has been demonstrated to enhance balance, cultivate core strength, and boost flexibility in older adults. Excellent Pilates exercises for older adults include mermaid movement, side circles, foot slides, step-ups, and leg circles.
Walking
Walking is one of the least stressful and easily accessible forms of exercise. However, walking challenges vary among seniors, so distance and step goals are individualized. Here are some suggestions for walking exercises for seniors:
- Explore a moderate trail through a park.
- Consider participating in a walk-friendly race to train.
- Walk around the perimeter of a familiar building.
- Listen to an audiobook or playlist for stimulation during your walk.
Bodyweight Exercises
Bodyweight exercises offer seniors effective ways to combat muscle loss, a common concern among older adults that can lead to hormone imbalances and protein metabolism issues. With around a third of seniors experiencing severe muscle loss, maintaining muscle strength is crucial. Bodyweight workouts are particularly beneficial for seniors as they are affordable and require minimal equipment, usually just workout clothes and a mat for floor support. Some recommended bodyweight workouts for seniors include squats to chair, step-ups, bird dogs, lying hip bridges, and side-lying circles.
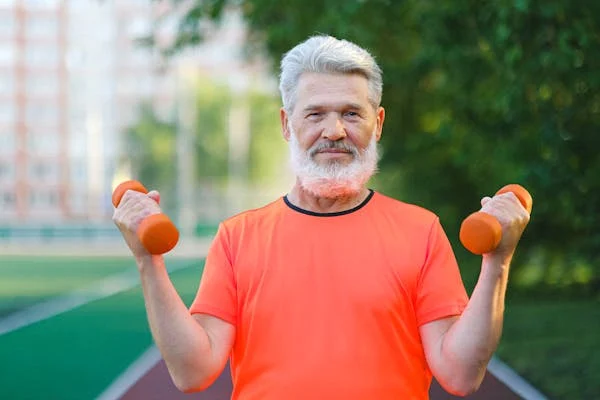
Dumbbell Strength Training
Dumbbell strength training offers seniors numerous benefits, including alleviating symptoms associated with diabetes, osteoporosis, back pain, and depression and aiding in weight management. It also boosts metabolism and enhances glucose control. When performed with proper precautions, dumbbell exercises are among the best ways for seniors to engage in strength training. Dumbbells enable seniors to isolate muscle groups for strength improvement while enhancing balance and flexibility.
Recommended dumbbell workouts for seniors include bent-over row, tricep extension, bicep curl, overhead press, and front raise.
Benefits of Senior Strength Training:
Strength Training Enhances Bone Health
Strength training exercises exert mechanical stress on bones, stimulating the production of new bone tissue and increasing bone density. This reduces the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, bolstering overall bone health.
Strength Training Increases Metabolic Function
Beyond the immediate physical gains, strength training boosts metabolism, leading to better weight management and healthier body composition.
Strength Training Improves Joint Flexibility
Targeted exercises build Strength and enhance joint flexibility, promoting greater ease of movement and reducing the risk of injury, especially for seniors prone to joint-related issues.
Although strength training offers functional and cognitive advantages, only a minority of adults and older adults engage in it twice weekly with ample intensity. Exercise-based active video games (exergaming) enhance exercise’s cognitive benefits and bolster adherence and motivation to training. Nevertheless, the potential advantages of a carefully prescribed and supervised strength training regimen, combined with concurrently or sequentially cognitive tasks, have yet to be considered.
Cognitive Benefits of Senior Strength Training:
While often underestimated, regular strength training has positively impacted cognitive function, improving mental acuity and overall brain health.
Strength Training Enhances Functional Abilities
Strength training isn’t solely about bulking up muscles. It directly translates into improved daily functions for seniors, allowing them to perform everyday tasks more efficiently and confidently.
Initiating a Senior Strength Training Regimen
Senior Strength Training Consultation and Safety
Before embarking on any exercise regimen, especially for seniors, it’s crucial to consult healthcare professionals to create a safe and tailored training plan that considers individual health conditions and limitations.
Progressive Strength Training Methods
Gradual progression is critical in senior strength training to prevent injury and maintain motivation. Starting at an appropriate level and gradually increasing intensity ensures a sustainable and safe training program.
Strength Training’s Nutritional Support
An essential companion to strength training is a balanced and supportive diet. Nutritional needs change with age, and an adequate diet plays a crucial role in supporting the body through the rigors of training and overall health maintenance.

Overcoming Challenges in Senior Strength Training:
Addressing Misconceptions
There exist myths and misconceptions surrounding senior strength training, often deterring individuals from reaping its benefits. Debunking these misconceptions is crucial in encouraging participation.
Adapting to Physical Limitations
Every individual has unique physical limitations, so tailoring workouts accordingly is essential. Adapting exercises to accommodate these limitations ensures a safe yet effective workout routine.
Consistency and Motivation
Consistency is the cornerstone of progress in any training program. Motivation often fluctuates, especially in long-term commitments. Strategies to maintain consistency and motivation are pivotal for success.
Realizing Age-Defying Strength:
Testimonials and Success Stories
Real-life success stories and testimonials from individuals who have transformed their lives through senior strength training inspire others to embark on a similar journey.
The Role of Community and Support
A supportive community, whether through group exercise classes or online forums, can be a tremendous source of motivation, advice, and encouragement for seniors navigating their strength training journey.
Reaping the Rewards
The culmination of dedication to senior strength training yields multifaceted rewards, transforming not just the body but also the mind, fostering a renewed sense of vitality and well-being.
Conclusion:
Senior strength training is the path to age-defying vitality. It is a beacon of hope for individuals seeking to redefine their aging experience. Its impact extends beyond physical Strength, touching on various aspects of health and well-being, inviting all to embrace its transformative power.
Aging need not be synonymous with decline; it can be a chapter marked by resilience, Strength, and vitality. The journey through senior strength training is a testament to the possibilities of reclaiming one’s Strength and rewriting the narrative of aging.




